Oracle Sharding is now available in Oracle Cloud with Oracle Database Cloud Service as well as Kubernetes and Docker containers (OKE).
Oracle Sharding enables hyperscale, globally distributed, converged databases. It supports applications that require linear scalability, elasticity, fault isolation and geographic distribution of data for data sovereignty.
It does so by distributing chunks of a data set across independent Oracle databases (shards). Shards can be deployed in the cloud or on-premises and require no specialized hardware or software.
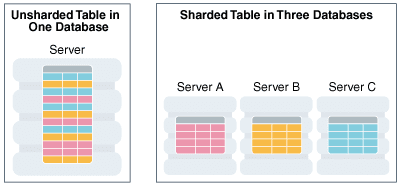
The following figure shows a table horizontally partitioned across three shards.
Figure 1-1 Horizontal Partitioning of a Table Across Shards
Benefits of Sharding
◉ Linear Scalability. Sharding eliminates performance bottlenecks and makes it possible to linearly scale performance and capacity by adding shards.
◉ Fault Containment. Sharding is a shared nothing hardware infrastructure that eliminates single points of failure, such as shared disk, SAN, and clusterware, and provides strong fault isolation—the failure or slow-down of one shard does not affect the performance or availability of other shards.
◉ Geographical Distribution of Data. Sharding makes it possible to store particular data close to its consumers and satisfy regulatory requirements when data must be located in a particular jurisdiction.
◉ Rolling Upgrades. Applying configuration changes on one shard at a time does not affect other shards, and allows administrators to first test the changes on a small subset of data.
Unlike NoSQL solutions, Oracle Sharding provides strong data consistency, the full power of SQL, support for structured and unstructured data, and the Oracle Database ecosystem.
Source: oracle.com




0 comments:
Post a Comment