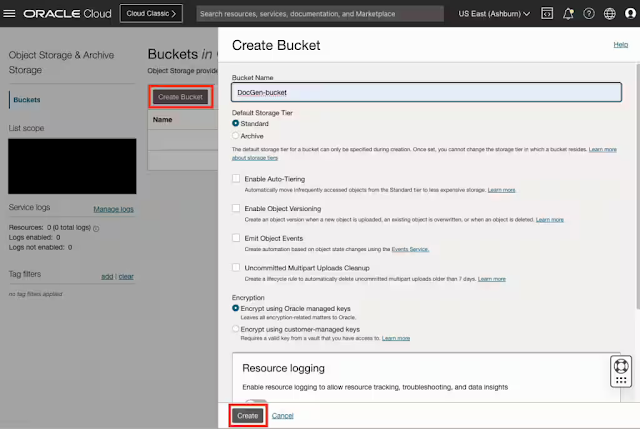
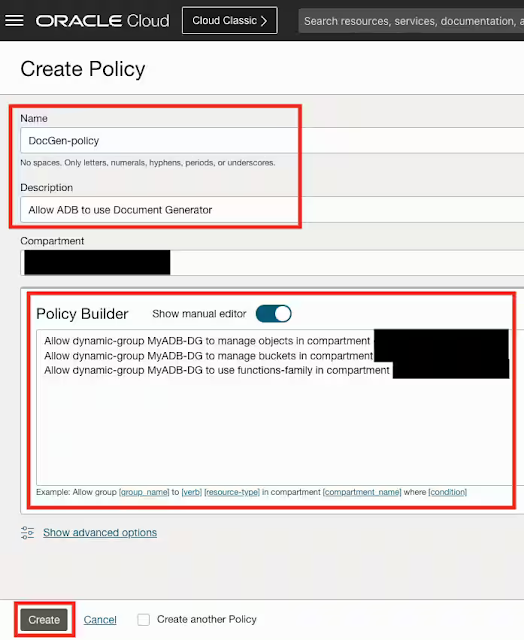
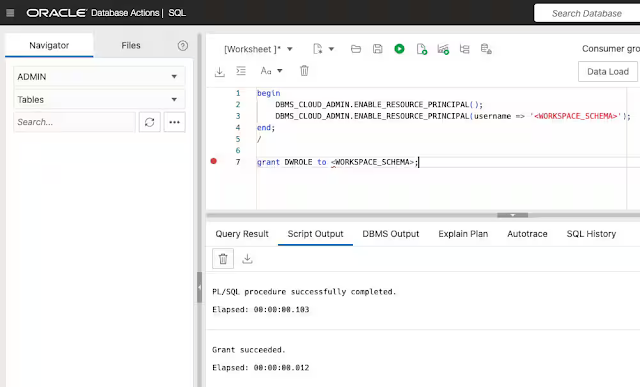
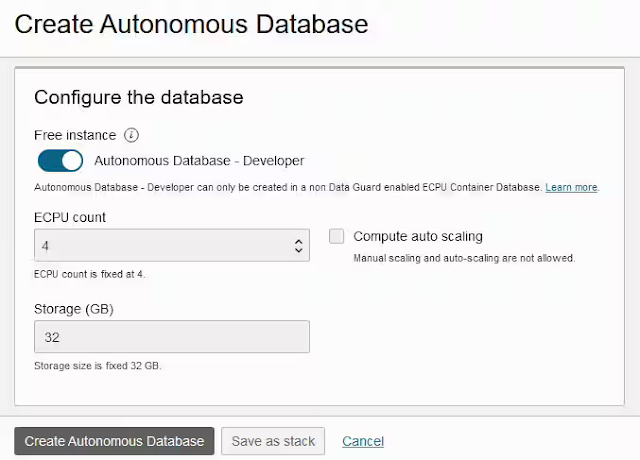
Analytics operations, or AnalyticsOps for short, is a concept that has evolved beside the advent of cloud computing, democratized analytics, and advanced analytics techniques such as AI/ML. Don't confuse AnalyticsOps with Operational Analytics, which is an entirely different concept, nor the older concept of the BI center of excellence (BICOE). AnalyticsOps works alongside, and doesn't replace, DevOps and MLOps to improve business outcomes. Implementing AnalyticsOps as a formal function is a key step in the journey to achieve analytics-mastery.
What is AnalyticsOps (analytics operations)?
AnalyticsOps is a set of operational and administrative processes, tools, and tasks for an analytics platform deployment. It involves the integration of analytics and operations to drive user adoption, improved analytics and KPIs, better decision-making, and optimization of business processes toward achieving strategic goals. In simpler terms, AnalyticsOps is the practice of using data analytics and operational tools to increase the value of an analytics platform and achieve desired outcomes. AnalyticsOps enables organizations to collect, process, analyze, and act on data in real-time. AnalyticsOps aims to create an analytics-driven culture within the organization, where data is integrated into decision-making at all levels - from daily operations to strategic planning - to optimize efficiency, minimize costs, and maximize revenue.
For example, Oracle has a dedicated Global Revenue Operations (Rev Ops) team responsible for developing and maintaining the Oracle Global Analytics, Reporting, and Sales Intelligence Platform (SI), which supports over 11,000 internal stakeholders from various departments, including sales, marketing, and finance. The team proactively monitors a wide range of AnalyticsOps KPIs using Oracle Analytics Cloud (OAC), ensuring that all queries essential to the monthly review process have a maximum response time of 5 seconds. This level of service has led to increased efficiency and accuracy, because Oracle's sales management has agreed to review live data during meetings instead of relying on error-prone spreadsheets or slide show presentations.
Additionally, the Rev Ops team analyzes poorly performing queries and reaches out to the specific users who initiated the request, offering to help them build more efficient queries. By examining the telemetry data of the OAC instance, the team can identify opportunities for efficiency, such as educating users on scheduling data flows to not run jobs hourly when the source data system updates every 24 hours, which can help reduce the operational load on the system. These efforts have had a significant positive impact that has led to improved stability and performance of the analytics platform, especially given the large and active user community of over 11,000 stakeholders.
How is AnalyticsOps related to DevOps and MLOps?
DataOps focuses on streamlining and automating data pipelines to improve the speed and quality of analytics. MLOps is an extension of DataOps that specifically addresses the unique challenges of deploying and managing ML models at scale. Conversely, AnalyticsOps integrates analytics and operations specifically to improve the analtyics workflows to drive better decision-making and optimize business processes. All three - DataOps, MLOps, and AnalyticsOps - are crucial for business success in today's data-driven economy.
How does AnalyticsOps differ from the BI center of excellence?
The BI center of excellence (BIoE) is an older approached that creates a centralized team, usually residing with IT, responsible for managing the organization's business intelligence (BI) efforts, including data governance, data quality, reporting, and analytics. That team’s responsibilities included providing standardized reports and dashboards to business users, who then used this information to make decisions. Essentially, a BIoE established, deliverd, and maintained policies and processes that delivered a mode 1 (as defined by Gartner) style of analytics. The focus was on delivering content through a given BI tool but didn’t incorporate other operational aspects and technologies related to a comprehensive analytics deployment.
In 2016, Gartner declared that “the BICC is dead…” recognizing the evolving landscape of analytics tools, including the emergence of predictive technologies and the groundwork for machine learning (ML). Gartner's observation indicated that the successor to the BICC should prioritize empowering businesspeople with self-service capabilities through training, education, and coaching – which aligns with what we now know as AnalyticsOps.
AnalyticsOps takes a broader approach toward what Gartner refers to as mode 2 analytics. It integrates analytics and operations, including promotion of advanced analytics techniques such as AI/ML, to create an analytics-driven culture within the organization. Instead of relying on a centralized team to provide reports and dashboards, AnalyticsOps empowers business users to analyze and interpret data in real-time, allowing them to make faster, more informed decisions. In addition, it ensures all processes, policies, and tools are in place to ensure the deployment and availability of the analytics platform that supports modern analytics
How can AnalyticsOps help reduce “Data Debt?”
“Data debt” refers to the accumulation of data-related issues and problems that haven't been addressed or resolved over time, resulting in a backlog of work that IT hasn’t been able to complete. In the context of corporate data analytics, data debt can arise from incomplete or inaccurate data or data models, outdated data infrastructure, or inefficient data processes that haven’t been adequately maintained. This can impede an organization's ability to make informed analytics-driven decisions. To address data debt, organizations need to invest in data management and governance processes that ensure data quality, accuracy, and consistency for an analytics platform, which can help them make better decisions and stay ahead of the competition. By adopting an AnalyticsOps approach, organizations can better manage their data analytics processes and reduce the risk of accumulating data debt. This helps increase the accuracy and trustworthiness of data and analytics that support the decision-making process.
To illustrate, consider a digital marketing company that has been collecting customer data from multiple sources including social media, online orders, and service calls, over the course of several years. During this time, the company underwent changes such as switching database vendors, acquiring companies, and revamping their customer loyalty program, resulting in a significant amount of customer data stored across multiple locations in different formats. As a result, the business users struggle to report accurately on customers, often making mistakes due to inconsistent or incomplete data. In this scenario, the company is grappling with overdue issues, or data debt. By implementing AnalyticsOps, the company can address the root cause of its customer data problems by analyzing its current data definitions and creating customer data standards with improved automated data collection, cleansing, and validation processes. AnalyticsOps has simplified the customer data definitions, making it easier for business users to correctly access and report on their customers.
What are the benefits of AnalyticsOps?
Unlike DataOps and DevOps, AnalyticsOps takes into account the last mile of the data journey at the Analytics layer. Say goodbye to low adoption rates, lack of trust, high costs, and difficulties with regulatory compliance.
- Improved stability and performance: Stakeholders have greater confidence in using the analytics platform to make business decisions. Ensuring the best performance reduces time wasted waiting and instead focuses businesspeople on strategic tasks.
- Better analytics integrity: AnalyticsOps actively monitors queries and activity to ensure the integrity of the analytics platform by quickly identifying and resolving slow or malformed queries through updates to the data model or data source, or by providing end-user education.
- Better decision-making: By having access to accurate, timely, and relevant data, businesspeople make informed decisions by being data-driven based on data insights rather than assumptions or gut feelings. This improves accuracy of decision-making and reduces the risk of errors.
- Boosted user adoption: Success of the analytics platform can be directly measured in terms of user adoption. Higher adoption means better ROI on the analytics platform. AnalyticsOps benefits ensure the best user experience and business outcomes, which leads to greater usage (and adoption)
- Enhanced agility: AnalyticsOps can enable businesses to spot potential risks and to adapt quickly to market shifts and changing customer needs. Real-time data insights allow businesses to make quick decisions and adjust their strategies accordingly.
- More competitive advantage: By using data insights, businesses can gain a competitive advantage because through using techniques such as predictive analytics, they can take advantage of new and potentially unseen opportunities before their competitors.
- Increased efficiency: AnalyticsOps can help to automate analytics processes and workflows, reducing the time and effort required to collect, process, and analyze data. AnalyticsOps also helps with cleaning up the catalog (identifying and deleting unused workbooks, data flows, and datasets).
- Improved collaboration: AnalyticsOps can foster structured collaboration between different people within an organization, including IT, data science, and business groups. This leads to better alignment of objectives, as well as more effective communication and faster decision-making.
What are the costs of AnalyticsOps?
The costs of establishing AnalyticsOps aren't just limited to financial investments in analytics tools and technologies but are primarily indirect costs. These costs are associated with the time, effort, and resources required to provide AnalyticsOps and include:
- Training and upskilling: Establishing AnalyticsOps requires the upskilling of existing employees to enable them to understand not only analytics tools and technologies, but also the data sources and definitions across the organization’s data estate.
- Time and resources: Creating an analytics-driven culture requires investment of time and resources. This includes time spent on data collection, preparation, analysis, and interpretation, as well as the resources required to maintain data pipelines and systems.
- Data governance: AnalyticsOps requires a strong data governance framework to ensure that data is accurate, trusted, and secure. This requires additional effort and resources to develop and maintain.
- Change management: Implementing AnalyticsOps may require changes to existing processes and workflows. This can create resistance from employees who are accustomed to working in a certain way with certain tools (such as Microsoft Excel) and may require additional time and effort to manage.
- Collaboration and communication: AnalyticsOps requires collaboration between different teams within the organization, including IT, data science, and business groups. This requires effective communication and coordination, which may be challenging to establish and coordinate.
Summary
AnalyticsOps is a critical and proactive methodology that integrates analytics and operations to improve business outcomes, to drive user adoption, and to achieve strategic goals. It's a decentralized approach that empowers business users to analyze and interpret data in real-time, allowing them to make faster, more informed decisions. AnalyticsOps also emphasizes the importance of agility and continuous improvement. It uses automation and machine learning to streamline data processes and optimize business performance. This enables organizations to quickly adapt to changing market conditions and stay ahead of the competition. It's a key step in the journey toward analytics-mastery, and organizations that embrace it will thrive in the data-driven economy.
Source: oracle.com