Moving your on-premises workloads to the cloud can offer many benefits, such as downsizing data centers, eliminating infrastructure management, accelerating application deployments, simplifying administration with automated and autonomous services, and lowering cost. If you’re ready to start moving existing Oracle databases to the cloud, it’s important to carefully evaluate your requirements to determine which cloud provider can best meet your application and operational needs.
Here are some key questions you should consider before migrating your Oracle databases to the cloud:
1. Does the cloud service support your database requirements?
2. Can you achieve the required service levels?
3. How will you meet your compliance requirements?
4. What security controls are available to protect your data?
5. What are your options for migrating your databases?
6. What is the cost impact?
Let’s discuss each of these in more detail.
1. Does the cloud service support your database requirements?
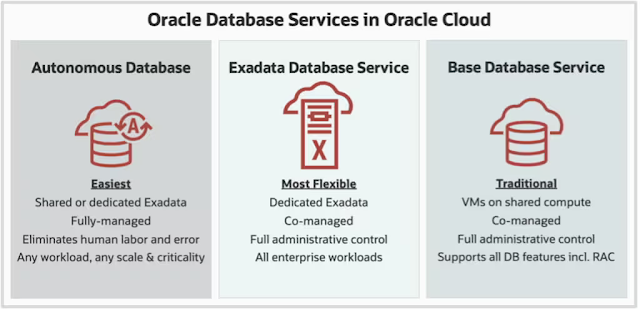
Although many of you are developing new cloud-native applications, you will still need to migrate existing on-premises applications to the cloud. The easiest approach that requires the least amount of effort is to move your applications with no changes. If your applications are already written for Oracle Database, you should ensure your cloud service provider supports it without compromises. For example, if you are running Oracle Database with Oracle RAC on-premises, it’s important to choose a cloud service that can support all of the Oracle Database features that you currently use. Oracle Cloud is the only cloud that offers Exadata, Autonomous Database, and supports Oracle RAC - enterprise-grade functionality essential for many customers moving their critical workloads from on-premises to the cloud. For those already committed to other clouds, multicloud offerings such as the Oracle Database Service for Azure, allow you to benefit from database services in Oracle Cloud with your applications running in other clouds.
2. Can you achieve the required service levels?
Ensuring you choose a cloud provider that enables you to achieve your required service levels is another critical factor to consider before migrating your databases to the cloud. You’ll especially want to consider your options carefully if your applications require high performance, are critical to your operations, and protect vital data. Migrating to a cloud that cannot match or exceed your on-premises performance, reliability, security, and operational requirements could spell disaster for your organization. Doing the research upfront to select a cloud provider that meets your needs will save you the headaches associated with migrating to the cloud and struggling to meet your required service levels.
Oracle offers cloud database services to meet any workload requirement starting with Oracle Database on standard virtual machines. For more demanding requirements, Oracle offers the performance, availability, and security of its premier Exadata platform as cloud infrastructure, which serves as the foundation for Autonomous Database and Exadata Database Service. Oracle Cloud automation deploys Oracle Database services with Maximum Availability Architecture (MAA) best practices uniquely featuring Oracle RAC to improve your service levels. Autonomous Database deploys all MAA best practices automatically to provide the highest service levels.
3. How will you meet your compliance requirements?
Compliance is another area you must consider before making the decision to migrate your databases to the cloud. Oracle is committed to helping address an ever more complex regulatory environment by providing information regarding industry-standard programs that demonstrate how Oracle Cloud services adhere to compliance programs. These programs can assist in your compliance and reporting, providing an independent assessment of the security, privacy, and compliance of Oracle Cloud services.
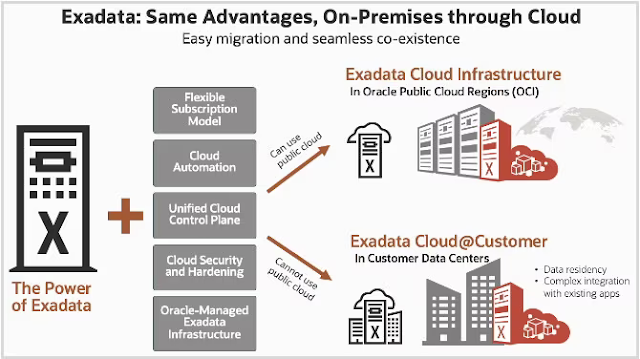
Many industries are subject to additional compliance requirements that can prevent public cloud adoption, such as the requirement for full physical control over data, and in some cases limitations on where data may be geographically stored. To meet the needs of customers who cannot bring their data to the public cloud, Oracle offers Exadata Cloud@Customer, which brings the cloud to customer data centers. It provides cloud benefits while meeting stringent data residency requirements. Since the data is stored in customer data centers next to existing on-premises applications, customers can also easily maintain their current system dependencies.
4. What security controls are available to protect your data?
Security is top of mind for anyone migrating to the cloud. Data protection from external threats or misuse, plus monitoring and auditing tools, are critical for your organization. Oracle’s comprehensive defense in depth security strategy integrates preventive, detective, and responsive security controls throughout the entire stack - not just the database. These include authentication controls for databases, virtual machines, and infrastructure; isolation controls for networks; and encryption for data at rest and in transit. Infrastructure and database maintenance is also a key component of data protection. Infrastructure for all Oracle Database services is maintained by Oracle. Database updates are regularly released for the co-managed database services. Since Autonomous Database is a fully-managed service, the latest updates are automatically applied with zero downtime.
In addition to external threats, some customers may be uncomfortable with a cloud provider’s access to infrastructure and services they use. Since cloud providers may have elevated privileges, maintaining security and isolation requires additional controls. To address this concern, Oracle provides Operator Access Control (OpCtl) to limit access by Oracle Cloud Operations to sensitive systems and their underlying infrastructure. With OpCtl, customers approve operator access with reduced privileges to specific components for a period of time. Customers can also monitor access with command and keystroke auditing as well as revoke access permissions. These additional protections address compliance requirements for customers in regulated industries such as utilities and financial services, which removes a previous impediment to cloud service adoption. To enable customers to offload administration, Database Vault is used with Autonomous Database to provide secure isolation between customer data and Oracle Cloud Operations. Database Vault can also be used with all Oracle Database services to enforce customer policies for data access. To further help customers manage security and compliance requirements, Oracle includes Data Safe with all Oracle Database services in Oracle Cloud to provide security and user privilege assessments, drift detection, database auditing, and much more.
These are just a few examples of the security controls available in Oracle Cloud that help protect your data.
5. What are your options for migrating your databases?
Migrating your applications to the cloud impacts your entire stack including your databases. You can migrate the entire stack as is, make small improvements, or re-architect it as part of your cloud journey. The amount of effort required and your tolerance for application disruption will help determine the type of database migration to pursue. Since Oracle Database is 100% compatible between on-premises and cloud deployments, all you need to do is move the data.
With Oracle Database you can use familiar migration methods, such as backup and recovery, provided you can tolerate some downtime. Since downtime can be a problem for critical databases, Oracle offers an automated solution using Zero Downtime Migration (ZDM) to simplify your database migration. ZDM can be used to deploy a replica database in Oracle Cloud, synchronized with your production database on-premises. Once you are ready, you switch your applications to the cloud database to complete your cloud migration.
6. What is the cost impact?
Cloud deployments can provide efficiency, reduced management, and automation of common tasks that lower operational costs. However, not everyone who moves their databases to the cloud experiences a reduction in total costs – often because of the database service and cloud provider they select. To fully benefit from the cost reductions associated with migrating Oracle databases to the cloud, you should select database services that provide superior performance, let you pay only for what you use, reduce complexity through consolidation, and allow you to bring your own licenses.
Superior performance enables you to use less infrastructure, but it’s also important to align license spend with your actual requirements. Rather than operating servers in the cloud that are configured to handle peak workloads, Oracle enables you to adjust compute resources as required for Oracle Database services in Oracle Cloud. Autonomous Database automatically scales compute resources in real time as workload requirements change – all without impacting database availability. Exadata Database Service supports user initiated online compute resource scaling and provides APIs to automate scaling based on resource utilization. The pay-for-use elasticity of Autonomous Database and Exadata Database Service can dramatically reduce your Oracle Database licensing costs over time.
Database consolidation is another way to lower your total database costs, by reducing the total amount of cloud infrastructure resources. In the same way that dynamic resizing of database consumption helps reduce licensing costs, database consolidation enables you to improve infrastructure utilization. Analyst studies from ESG, Wikibon, and others have shown that database consolidation on Exadata in Oracle Cloud significantly reduces complexity and overall costs while still meeting your performance objectives. Dynamic scaling of database consumption coupled with database consolidation provides the most cost-effective way of running mission-critical databases. With Oracle Cloud, you also have the choice of license-included or bringing your own licenses to the database services for all Oracle Database Enterprise Edition features. Providing license mobility enables you to leverage your on-premises Oracle Database investments.
Key Takeaways
There are many considerations involved in migrating Oracle databases to the cloud. The right cloud provider must meet your performance, reliability, security, compliance, migration, operational, and cost requirements. Oracle Cloud eliminates many of the pitfalls that can hinder your cloud database migration. Running Oracle Database with its converged capabilities in the Oracle Cloud not only reduces complexity and simplifies application development, but can also provide the benefits of the fully-managed Autonomous Database, the performance of Exadata, and Oracle’s second generation cloud infrastructure that optimizes MAA. Oracle has decades of experience delivering technologies that support enterprise-grade database workloads on-premises. With careful planning, you too will be successful in migrating your on-premises Oracle databases to the cloud.
Source: oracle.com





0 comments:
Post a Comment