What is the Network Path Analyzer?
Network Path Analyzer (NPA) supplies a unified and intuitive capability you can use to find virtual network configuration issues that impact connectivity.
NPA collects and analyzes the network configuration to decide how the paths between the source and the destination function or fail. No actual traffic is sent, instead, the configuration is examined and used to confirm reachability.
Benefits of the Network Path Analyzer
Many network issues are caused by misconfiguration. Having a good tool to analyze and verify the network configuration can directly improve the efficiency of the entire troubleshooting process and significantly reduce the MTTR.
The Network Path Analyzer can quickly diagnose the routing and security policy configuration and tell you if a broken reachability is caused by misconfiguration. If it is, the Network Path Analyzer also tells you what is missing or wrong in the configuration, either incorrect routing, or lacking a required security rules in an NSG or security list.
Assumptions
All names and addresses used in this post are for examples only.
Privileges
Oracle recommends that you always set the following permissions policies at the tenancy level to use the Network Path Analyzer:
allow group <group-name> to manage vn-path-analyzer-test in tenancy
allow any-user to inspect compartments in tenancy where all { request.principal.type = 'vnpa-service' }
allow any-user to read instances in tenancy where all { request.principal.type = 'vnpa-service' }
allow any-user to read virtual-network-family in tenancy where all { request.principal.type = 'vnpa-service' }
allow any-user to read load-balancers in tenancy where all { request.principal.type = 'vnpa-service' }
allow any-user to read network-security-group in tenancy where all { request.principal.type = 'vnpa-service' }
Where <group-name> is the name of the administrator group for networking resources.
Using the Network Path Analyzer
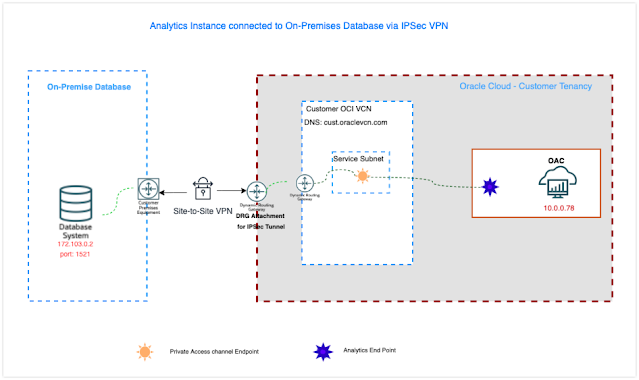
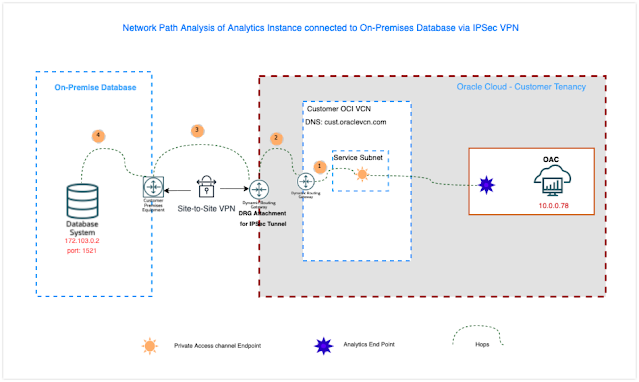
The following diagram shows an Analytics Instance connected to an on-premises database.
If you want to confirm that the logical network paths match your intent or verify that the virtual network connectivity setup works as expected before starting to send traffic or troubleshooting routing and security misconfigurations that might be caused due to connectivity issues.
To achieve any of these goals, create a test that you think should work and then run the test. You can also save this test definition to run it again later. Saved tests are displayed on the Network Path Analyzer page for you to select.
The following source and destination scenarios are supported:
◉ OCI to OCI
◉ OCI to on-premises
◉ On-premises to OCI
◉ Internet to OCI
◉ OCI to internet
Steps to Create a Network Path Analysis
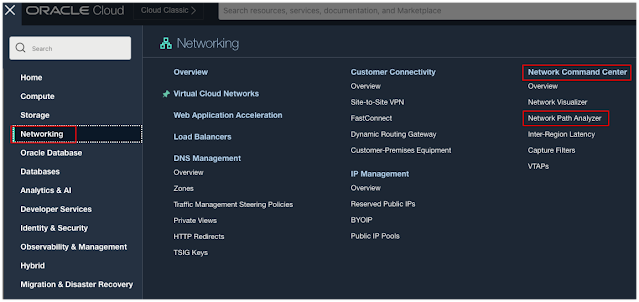
1. Login to OCI Console, Open the navigation menu, click Networking, and then click Network Path Analyzer, found in the Network Command Center group.
2. Click Create Path Analysis.
3. Assign the following parameters and attributes to the analysis:
3.1 Name: A descriptive name for the Network Path Analysis.
3.2 Create in Compartment: The default is the current viewing compartment.
3.3 Protocol: You can choose TCP, UDP, ICMP, SSH, or any other protocol type. You can also specify the source and destination ports.
3.4 Source: Select a resource that begins the path you are testing.
3.5 Destination: Select a resource that ends the path you are testing.
3.6 Test-Direction: Choose between Bi-directional to test both the forward and reverse paths, or Uni-directional to test the forward path only.
4. Click Run analysis.
Step 1: Log in to the OCI Console, Open the navigation menu, click Networking, and then click Network Path Analyzer, found in the Network Command Center group.
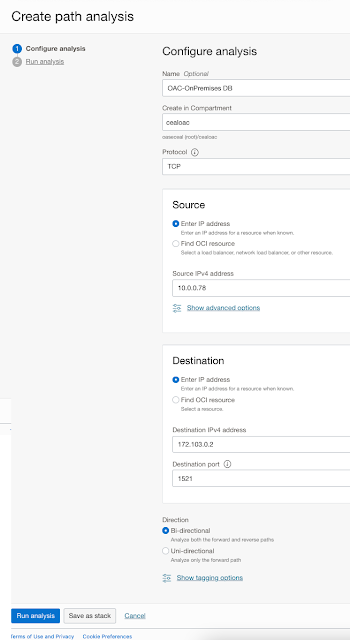
Step 2: Click Create Path Analysis, confirm you are in the Compartment you want to be in
Step 3: Configure Analysis
Source: Oracle Analytics Cloud (OAC) with PAC Configured, PAC Egress IP address: 10.0.0.78
Destination: On-premises DB IP Address: 172.103.0.2, port: 1521
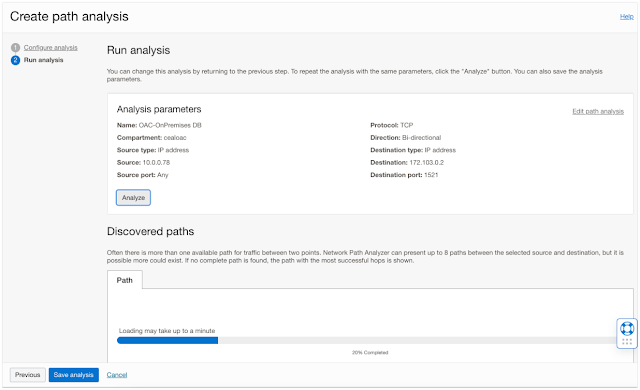
Step 4: Click Run Analysis
Loading may take up to a minute.
See the Discovered Paths to make sure the logical network paths match your intent or verify that the virtual network connectivity setup works as expected before starting to send traffic.
Forward path:
Return Path:
A hop occurs when a packet is passed from one network segment to the next.
The following diagram shows the hops between the source and the destination.
The hop count refers to the number of networks or network devices through which data passes between source and destination.
In this scenario, we can see the number of hops from the source (OAC) to the destination (DB) and the path it takes.
Source: oracle.com







0 comments:
Post a Comment