Exadata Cloud quarterly infrastructure maintenance, including software updates to the database server hosts, storage servers, and fabric switches is an Oracle-managed, automated process. The OCI control plane provides customer controls, until now primarily consisted of scheduling capabilities, for when and how the maintenance is performed. The Exadata software updates are applied in a rolling manner, node by node, and for the database servers, this includes a graceful shutdown and restart of each VM. Continuous availability for applications using databases hosted on the VMs can be achieved following MAA best practices for RAC rolling updates. However, you may have a legacy application that does not follow best practices and can experience impact during maintenance.
With this release, customers are now able to mitigate this impact through improved controls and visibility into the infrastructure maintenance process.
Key Benefits
With the enhanced quarterly infrastructure maintenance controls and visibility, you now get the following benefits:
1. Mitigate maintenance impact by enabling custom actions, performed by you outside of Oracle's purview, before starting the maintenance on each database server. Maintenance will wait, prior to shutting down the VMs on each database server, until a user resumes the maintenance or until the customer-configured timeout.
2. Plan better for maintenance by viewing the database server update order and estimated maintenance time for each database server and other components.
3. Track maintenance progress at a component level via work requests and OCI event subscriptions, which may be used to trigger customer-created automation for custom action performed during maintenance.
4. Minimize the overall maintenance window with the option for non-rolling maintenance.
OCI Console Experience
We will go over the following core, user-journey highlights for configuring the new infrastructure maintenance controls and viewing the additional maintenance progress details using the OCI console:
1. Edit maintenance preferences, including the maintenance method and the custom action configuration, for maintenance scheduled in the future.
2. Edit the maintenance method and custom action configuration, and view target versions and estimated time detail for a scheduled maintenance run.
3. Edit the custom action configuration, resume the maintenance before the timeout expires, and view maintenance progress for an in-progress maintenance run.
1. Edit maintenance preferences, including the maintenance method and the custom action configuration, for maintenance scheduled in the future
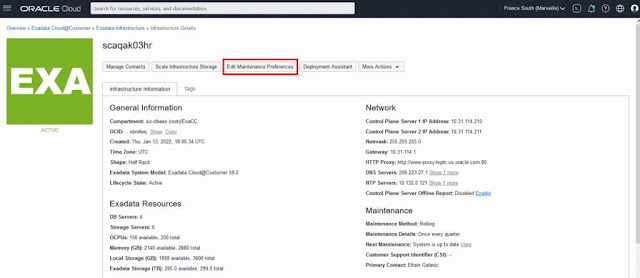
From the Exadata Infrastructure details page, click the new Edit Maintenance Preferences button.
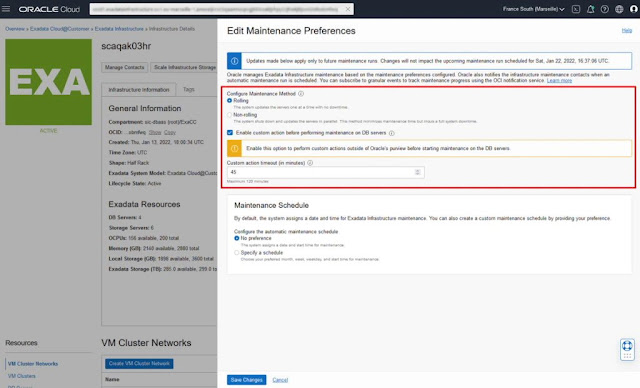
From the Edit Maintenance Preferences panel, configure the maintenance method between Rolling and Non-rolling. Rolling is the default and previously was the only method available. Rolling maintenance updates servers one by one while continuing to maintain the availability of the underlying RAC databases. Non-rolling maintenance shuts down and updates servers in parallel. This method minimizes maintenance time but incurs full system and database downtime.
From the Edit Maintenance Preferences panel, optionally enable custom action before performing maintenance on DB servers by clicking the associated checkbox. After clicking the checkbox enter the time, in minutes, for the custom action timeout. Enable custom action only if you want to perform additional actions, outside of Oracle’s purview, before starting DB server maintenance. For maintenance configured with the rolling method, enabling this option will force the maintenance run to wait up to the configured custom action timeout before starting maintenance on each database server. For maintenance configured with the non-rolling method, the maintenance run will wait up to the configured custom timeout before starting maintenance across all database servers.
The Edit Maintenance Preferences panel also provides the previously existing capability to configure a maintenance schedule.
2. Edit the maintenance method and custom action configuration, and view target versions and estimated time detail for a scheduled maintenance run
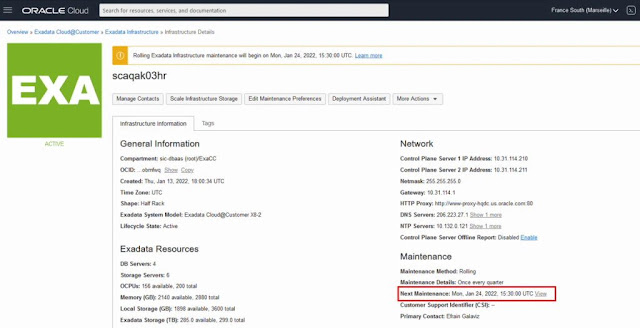
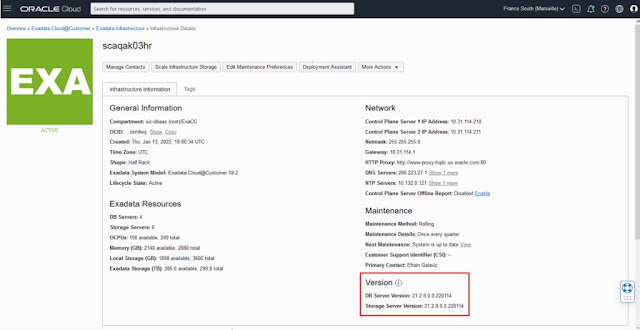
Once a quarterly infrastructure maintenance run is scheduled, the date and time will appear next to Next Maintenance under the Maintenance heading on the Infrastructure Details page. Click on the View link, next to the date, to view and edit the maintenance.
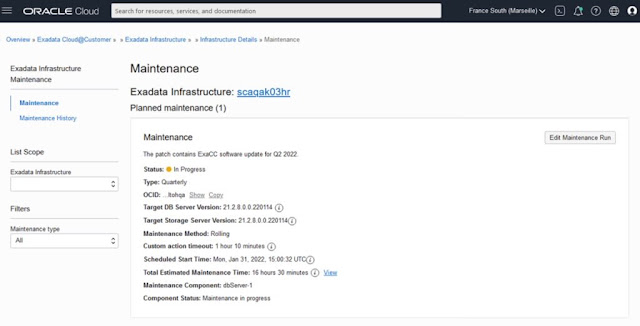
The Maintenance Details page now contains the configured maintenance method, custom action timeout, total estimated maintenance time, and the target database server and storage server versions, which will be applied by the scheduled maintenance. If the upcoming Exadata image version is not yet available, then the version information will say "LATEST". Once the upcoming version is available, the version information will be automatically updated to the specific Exadata image version to be applied by the scheduled maintenance.
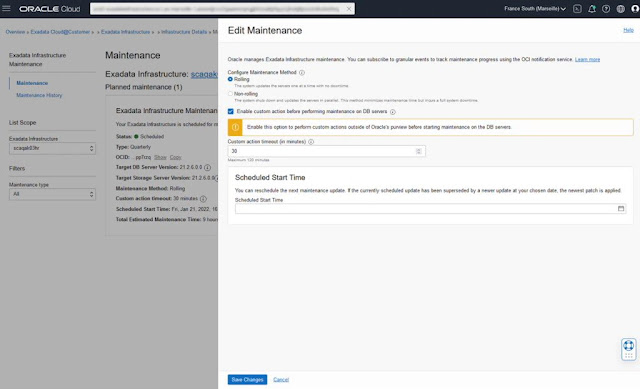
From the Maintenance Details page, click the "Edit Maintenance Run" button to configure the maintenance method and custom action, similar to the maintenance preferences, but for the scheduled maintenance run. This panel is also now the location to reschedule the start time for the maintenance.
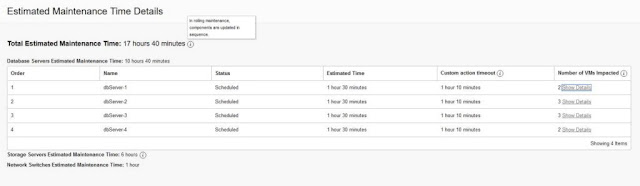
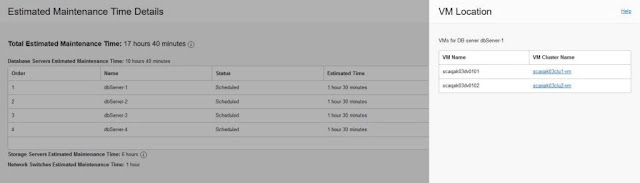
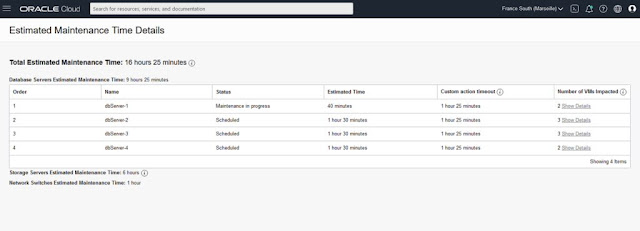
If the configured maintenance method is rolling, from the Maintenance Details page, click the View link next to the Total Estimated Maintenance Time. The Estimated Maintenance Time Details panel shows the total estimated maintenance time broken down at a component level including 1) the database servers estimated maintenance time and estimated time for each database server, 2) the storage servers estimated maintenance time, and 3) the network switches estimated maintenance time. The panel also displays the order in which each database server will be updated and shows the VMs that will be impacted during each database server's maintenance. Click on the Show Details under Number of VMs Impacted to open a panel listing each VM on the database server.
3. Edit the custom action configuration, resume the maintenance before the timeout expires, and view maintenance progress for an in-progress maintenance run
When a quarterly infrastructure maintenance run has started, the Exadata Infrastructure resource and the Next Maintenance will show as "Maintenance in Progress" on the infrastructure details page. Click on the View link next to the Next Maintenance field to view and edit the in-progress maintenance.
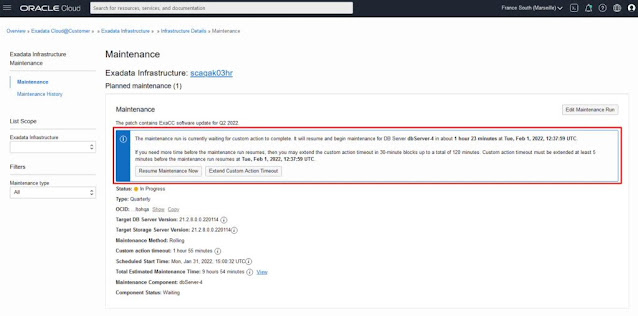
The Maintenance Details page, in addition to the fields available when the maintenance was scheduled, now displays the maintenance component and component status. These fields show what component is currently being updated and whether the maintenance is currently in progress for that component or, for the database server portion of the maintenance, if the maintenance is currently waiting for the custom action.
The Maintenance Details page, in addition to the fields available when the maintenance was scheduled, now displays the maintenance component and component status. These fields show what component is currently being updated and whether the maintenance is currently in progress for that component or, for the database server portion of the maintenance, if the maintenance is currently waiting for the custom action.
If the configured maintenance method is rolling, From the Maintenance Details page, click the View link next to the Total Estimated Maintenance Time. This page shows the progress of the maintenance at a component level. The estimated maintenance time is updated during the maintenance and the database servers will show Scheduled, Maintenance in progress, and Complete as the maintenance progresses through each server. The corresponding work request log messages and events generated through the OCI events service, are also available to track the maintenance progress at an individual component level - providing messages for the start and end of each custom action time, each database server, and other components.
Once the maintenance completes, the Exadata Infrastructure returns to an Active state, the version is updated on the Infrastructure Details page, and a record of the maintenance is displayed on the Maintenance History page, accessible from Maintenance details.
Considerations
◉ The best way to minimize the impact of Exadata Cloud infrastructure maintenance is to follow the Exadata Cloud MAA best practices on Achieving Continuous Availability for Your Applications. The custom action configuration is primarily meant as an additional control when the best practices cannot be followed.
◉ The custom action timeout may be configured or extended to a maximum of 2 hours (120 minutes), after which the automated maintenance will resume for the next database server.
◉ Currently, after the maintenance completes for a database server host, the automated maintenance will confirm the Oracle Clusterware (CRS) has started on each VM before shutting down the VMs and starting maintenance on the next database server. Other CRS resources (e.g. database instances/CDBs, PDBs, Listeners) are not confirmed to be up before moving to the next database server. The custom action configuration may be used to provide time for this if needed. Checks to ensure these resources have started prior to continuing to the next database server are planned for a future release.
◉ Rolling vs non-rolling maintenance method:
◉ Rolling maintenance is the default and begins with patching the Exadata database server hosts. Database servers are updated one at a time during which each VM on the host is shut down, the host is updated to the new version, restarted, and then the VMs are started. This process continues until all servers are updated. After database server maintenance completes, the storage servers are updated. Storage servers are updated one at a time and do not impact VM cluster VMs' availability.
◉ Non-rolling maintenance begins by shutting down all VMs across all VM clusters on the Exadata infrastructure. The storage servers are updated first and done all at the same time. The database servers are then updated after the storage server maintenance completes. Currently, the first database server is used as a driving server to update all other database servers at the same time. The first database server is then updated, after which all VMs are restarted prior to proceeding to the rolling network fabric switch updates.
Scope
This announcement is applicable to Gen 2 Exadata Cloud@Customer. The capability is planned for Exadata Cloud Service in a future release.
Availability
The enhanced infrastructure maintenance controls are now available on Gen 2 Exadata Cloud@Customer in all OCI commercial regions.
Source: oracle.com






0 comments:
Post a Comment