Oracle has adopted a new version numbering scheme. In addition, they have begun offering a new set of Autonomous Database services. With all the changes that have happened, it makes sense to step back and look at the offerings to determine what may be suitable for your Oracle database deployment.
In this article, we’ll demystify the version numbering changes, explore the Autonomous database solutions and differentiate between the two.
ORACLE DATABASE VERSION NUMBERING AND RELEASE CYCLE
Starting in 2018, Oracle has introduced a new version numbering schema that coincides with the year of the database software release. Oracle Database 18c was released in February 2018. In January of 2019, the Oracle 19c database was released.
It would be easy to be concerned that 18c and 19c represent major upgrades. However, this is not the case. 18c and 19c are both 12.2 releases of the Oracle database. Oracle Database 18c is Oracle 12c Release 2 (12.2.0.2). Oracle Database 19c is the long-term support release, with premier support planned through March 2023 and extended support through March 2026. Oracle 19c is essentially Oracle 12c Release 2 (12.2.0.3). Therefore, if you are considering an Oracle 12.2 Database deployment, you should consider an upgrade to the latest 12.2 release, which turns out to be Oracle 19c.
The new version numbering scheme utilizes a 3-tier designation and carries 2 digits for other purposes.
1. The first number in the version string designates the major release
2. The second a release update (RU)
3. The third a release update revision (RUR)
4. The fourth a release increment version
5. The fifth is reserved for future use
Major releases occur annually, corresponding to the year of release. The release update happens quarterly, numbered sequentially. Finally, the release update revision happens on as needed basis. An example version number, 19.3.0, would signify 19c as the major release, 3 as a third RU and 0 indicates the absence of an RUR. Oracle 18.6.0 is the 5th quarterly release and the 6th release overall.
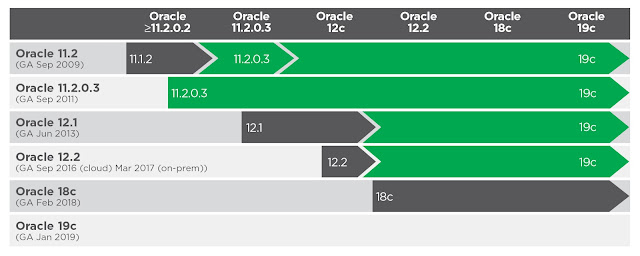
ORACLE DATABASE VERSION UPGRADE MATRIX
The matrix below details the upgrade path from legacy database releases to 19c. For the reader who is interested in upgrading directly to 19c, or plans an intermediate stop prior, this matrix is meant to provide information for planning.
The rows of the chart represent the major / point database release levels and communicate the GA release date. The columns contain release levels, represented as time moves forward.
The black arrow provides the minimum release level required to perform a direct upgrade to the next release level in relation to the initial release on the row. Then, any following green arrow shows the minimum release required to get to its direct upgrade version.




0 comments:
Post a Comment