We are pleased to announce the General Availability (GA) of VM Cluster Node Subsetting capability on Gen 2 Exadata Cloud@Customer. Previously, Exadata Cloud@Customer customers provisioned VM clusters across all DB servers in the Exadata Infrastructure and allocated resources from each DB server. With VM Cluster Node Subsetting, you have the flexibility to choose specific DB Servers to provision the VMs in your cluster and grow or shrink your VM clusters on-demand to meet your changing business needs.
Key Customer Benefits
With the VM Cluster Node Subsetting capability, you can now
1. Provision a new VM cluster with any number of VMs rather than hosting a VM on each DB server in the Exadata Infrastructure.
2. Start with a smaller VM cluster size at provisioning time, thereby enabling cost savings on resources allocated per VM.
3. Expand VM clusters to add VMs on-demand providing flexibility to scale resources without disrupting current running workloads.
4. Shrink VM clusters to remove VMs as needed to ensure efficient allocation of DB server resources.
5. Isolate VM clusters to run on specific DB Servers giving complete control over your isolation strategy for mission-critical workloads.
6. Co-locate VM clusters on specific DB Servers to implement efficient consolidation and streamline maintenance across your workloads.
7. Allocate resources from the new generation of DB servers to provision new VM clusters or extend the existing VM clusters to ensure optimal utilization of available resources.
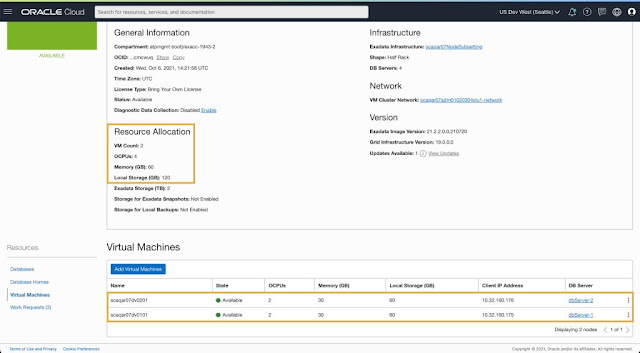
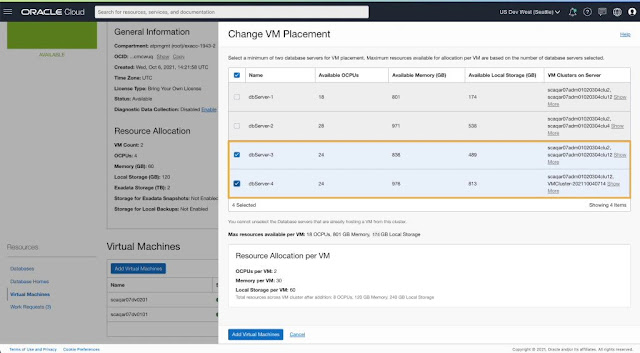
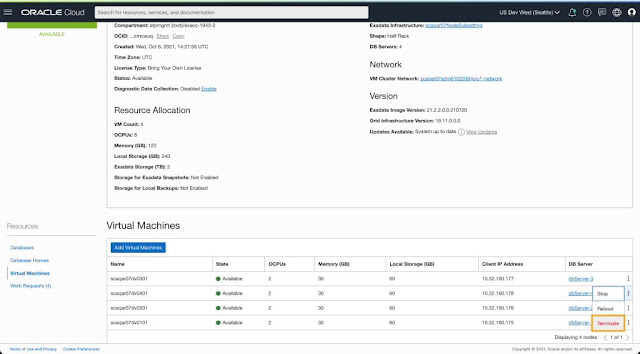
You can easily shrink existing provisioned VM clusters running on all DB servers in the infrastructure by terminating VMs running on specific DB Servers without affecting existing running workloads. Once the VM cluster is running on DB Servers of your choice, you can seamlessly scale resources (OCPU, memory, local storage) allocated per VM to ensure optimal resource utilization for the cluster. Newly provisioned VM clusters will only host VMs on selected DB servers. You can dynamically scale any VM cluster to add more VMs to the cluster or add more resources per VM based on changing workload requirements without disrupting your RAC-aware databases.
OCI Console Experience
Let's go over the following core user journey highlights related to VM cluster node subsetting using the OCI console.
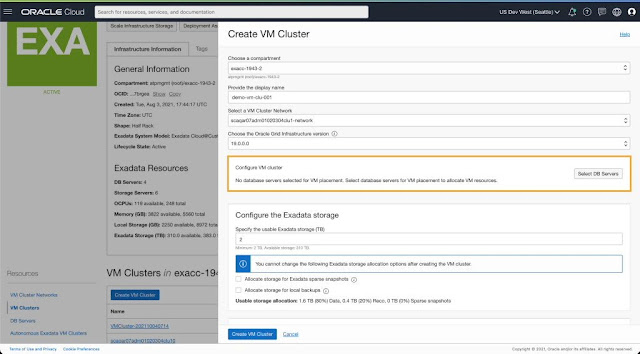
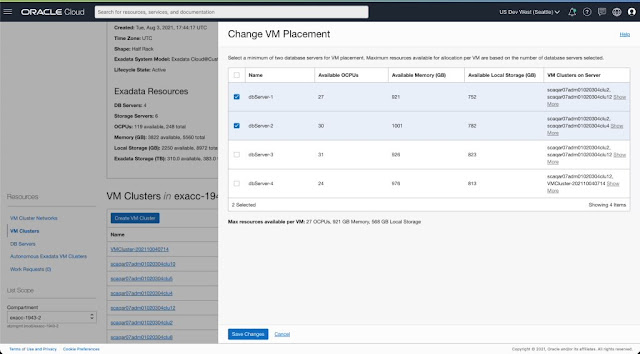
◉ Provision VM cluster on a subset of DB Servers
◉ Add or remove VM(s) to scale VM Cluster
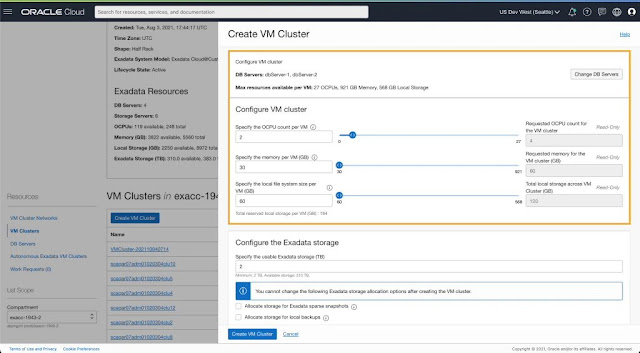
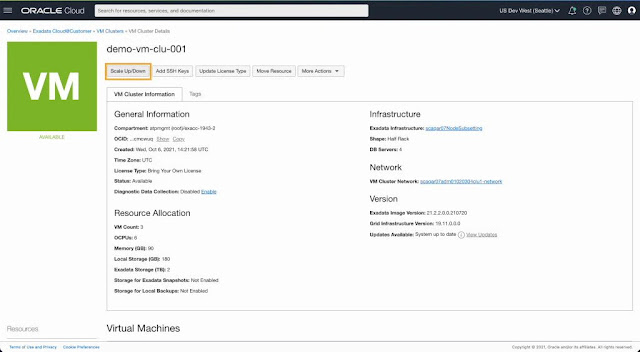
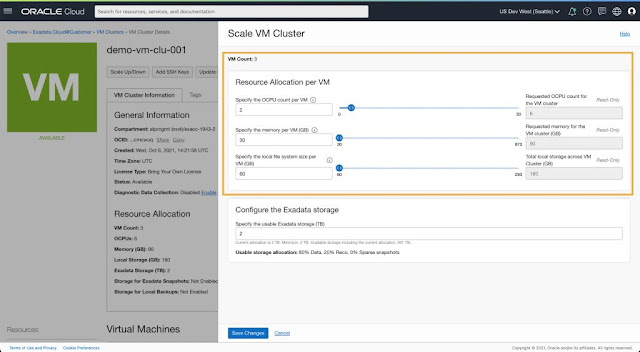
◉ Scale VM resources allocated to a provisioned VM cluster
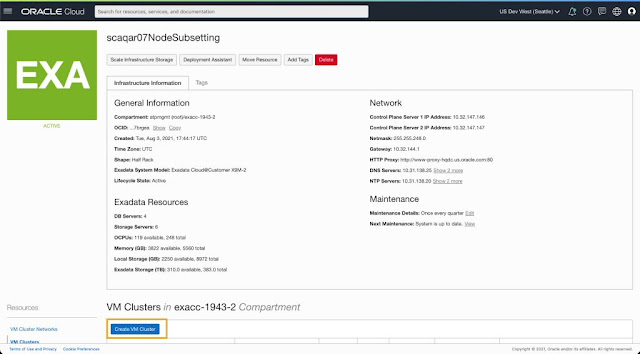
1. Provision VM Cluster on a subset of DB Servers
On the Exadata Infrastructure details page, you can navigate to the VM Cluster section and initiate the create VM Cluster workflow to provision a new cluster on this infrastructure.
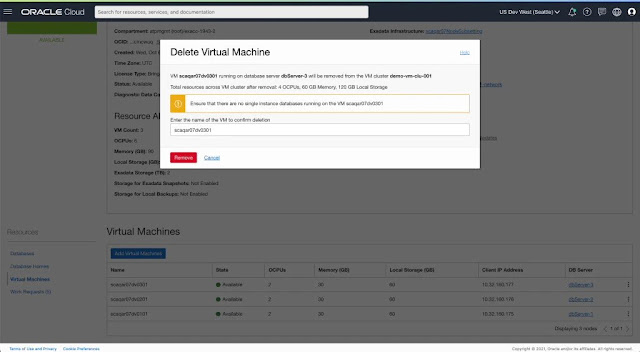
2. Add or remove VM(s) to scale VM Cluster
3. Scale VM resources allocated to a provisioned VM Cluster
Considerations
- VM Cluster Node Subsetting capability is available for new and existing VM Clusters in Gen 2 Exadata Cloud@Customer service.
- All VMs across a VM cluster will have the same resource allocation per VM irrespective of whether the VM was created during cluster provisioning or added later by extending an existing VM cluster.
- Any VM cluster should have a minimum of 2 VMs even with the node subsetting capability. We currently do not support clusters with a single VM.
- X8M and above generation of DB Servers can host a maximum of 8 VMs per DB Server. X7 and X8 generations can only support a maximum of 6 and 5 VMs per DB Server, respectively.
- Exadata Infrastructures with X8M and above generation of DB servers can support a maximum of 16 VM clusters across all DB servers. X7 and X8 generation Exadata Infrastructure DB Servers can only support a maximum of 12 and 10 VM clusters, respectively. The maximum number of clusters across the infrastructure depends on resources available per DB server and is subject to the per DB Server maximum VM limit.
- Every VM Cluster network is pre-provisioned with IP addresses for every DB Server in the infrastructure. One cluster network can only be used by a single VM cluster and is validated to ensure the IP addresses do not overlap with other cluster networks. Adding or removing VMs to the cluster does not impact the pre-provisioned IP addresses assigned to each DB server in the associated cluster network.
- The same Guest OS Image version running on the existing provisioned VMs in the cluster is used to provision new VMs added to extend the VM cluster. However, any customizations made to the Guest OS Image on the existing VMs must be manually applied to the newly added VM.
- For VM clusters running a Guest OS Image version older than a year, you must update the Guest OS Image version before adding a VM to extend the cluster.
- Adding a VM to a cluster will not automatically extend any database part of a Data Guard configuration (either primary or standby) to the newly provisioned VM. Terminating a VM from a cluster requires the removal of any database which is part of a Data Guard configuration (either primary or standby) from the VM to proceed with the terminate flow. Manual steps covered in MOS Note 2811352.1
- For databases not part of a Data Guard configuration, only databases that are running on all VMs in the existing cluster will extend automatically to the newly provisioned VM. Any database running on a subset of VMs will not extend automatically to run on the newly added VM.





0 comments:
Post a Comment