We are announcing new Pluggable Database (PDB) automation capabilities on Exadata Database Service on Cloud@Customer (ExaDB-C@C), Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure (ExaDB-D), and Base Database Service (BaseDB) in all OCI commercial regions. The new set of enhancements brings the automation via OCI Console/API/Terraform for the following PDB-specific features to the Exadata Database and Base Database services:
◉ Backup and restore
◉ Remote clone
◉ Refreshable clone
◉ Relocate
◉ View open modes per VM
Key Benefits
◉ Leverage new PDB automation capabilities for end-to-end application development and deployment in the cloud.
◉ Access Oracle Multitenant features via OCI Console/API/Terraform on Exadata Database Service and Base Database Service.
Let's go over the core user journeys!
Note: For ExaDB-C@C, ExaDB-D, and BaseDB services in the OCI console, we refer to Container Database (CDB) as 'Database'. Any mention of CDB below is for clarity and brevity only.
PDB backup
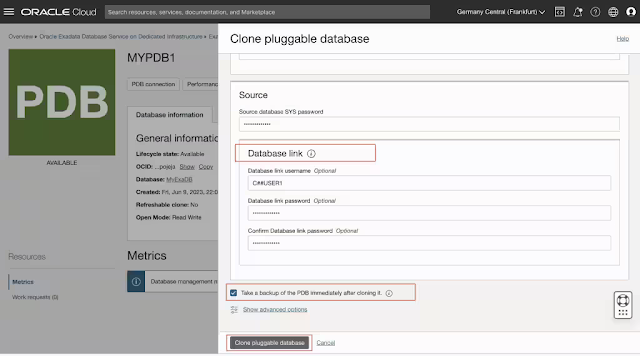
When you create a PDB, you can specify if you would like to take an immediate backup of that PDB. This option is also available during local clone, remote clone, and relocate operations if the CDB is configured with the auto-backup feature. The PDB backup destination will always be the same as that of the CDB, and the backups cannot be accessed directly or created on demand. Oracle recommends immediately backing up the PDB after you create, clone, and relocate it, to ensure your PDB is recoverable before the next CDB auto-backup is completed successfully.
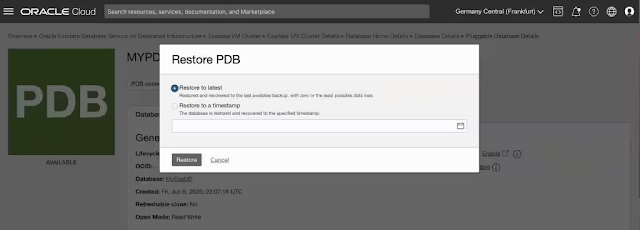
PDB restore - In-place and Out-of-place restore
You can now restore a PDB within the same CDB (in-place restore) or to a new CDB (out-of-place restore, applicable to ExaDB-D and BaseDB). In-place restore allows you to choose to restore to the latest or a specified timestamp. This is not applicable to PDBs on a Data Guard enabled CDB.
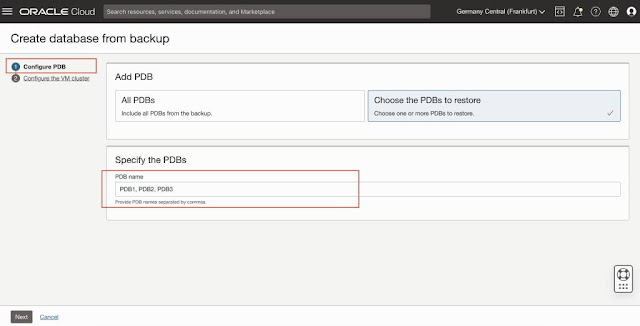
Out-of-place restore of a PDB(s) is achieved when you restore a PDB to a new CDB. 'Create database from backup' is enhanced to allow restore of a PDB or a set of PDBs to a new CDB. You can specify a PDB or a group of PDBs by the 'Choose the PDBs to restore' option. By default, the PDB(s) will always be restored on a new CDB to be created on an existing VM Cluster or in a new DB System.
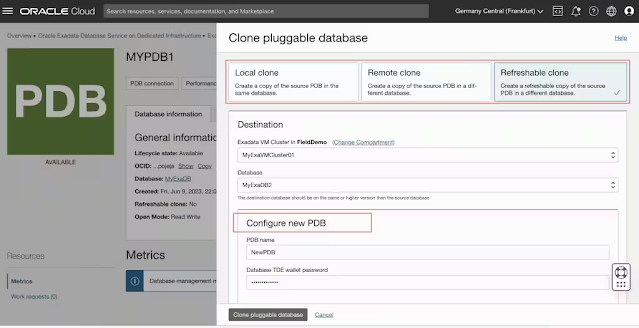
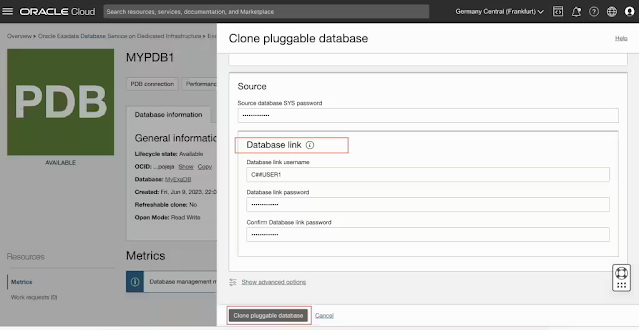
Remote clone
You can create a copy of the PDB within the same CDB (local clone) or to a different CDB (remote clone). The destination CDB can be of the same database version or higher. You can optionally provide an existing common user name (a user created in the CDB$root container) that the database link will use to connect. There is an option to take the backup of the PDB after remote cloning. PDB remote cloning works across Data Guard environments.
Refreshable Clone
You can create a refreshable copy of a PDB (refreshable clone). Providing an existing common user name is mandatory for the database link connection. A refreshable clone PDB can be refreshed at will by going to the PDB details page and initiating the action 'Refresh.' To be able to refresh successfully depends on the availability of the archive redo log files.
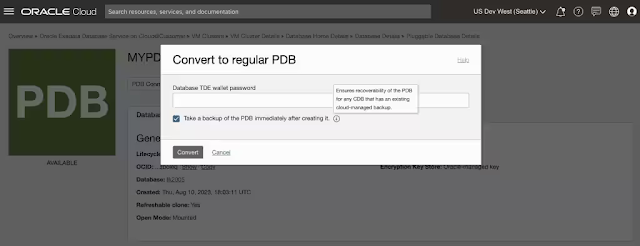
To disconnect the refreshable clone PDB from the source, you can convert it to a regular PDB. Once converted, the PDB will be opened read-write, and all the lifecycle operations can be performed. There is an option to take a backup of the PDB after converting from a refreshable clone to a regular PDB. The operation to convert a refreshable clone to a regular PDB when performed on a Data Guard primary will also create a PDB on its standby and be available in mount mode.
PDB relocate
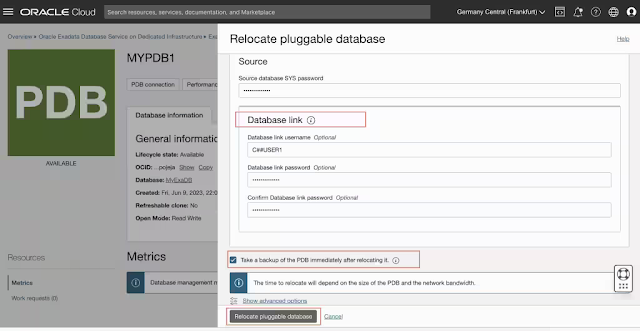
You can move a PDB to another CDB. The destination CDB can be in a different compartment, VM cluster, or DB system. The destination container database can be on the same database release version or higher. You can provide a new PDB name while relocating a PDB to a different CDB. Optionally provide an existing common user name the database link will use to connect. There is an option to backup the PDB after relocation to the destination CDB is complete. The time to relocate depends on the size of the PDB, and network bandwidth during file copy from source to destination. Once relocated, the PDB will be opened read-write on the destination. If the destination is a Data Guard primary, a PDB will be created on the standby and will be available in mount mode.
PDB open modes
A PDB can be opened on a specific VM (a database instance) in the case of a multi-node RAC CDB. If the open mode across the VMs is the same, you will see either of these values: Read Write, Read Only, Mounted. If the open mode across the VMs differs, you will see which VM PDB is opened in Read Write mode by hovering the mouse over the information icon. You cannot change the open modes of the PDB through the OCI console or API. However, you can start or stop a PDB. Starting a PDB and stopping a PDB will bring it into read-write and mount mode accordingly. On standby, starting a PDB and stopping a PDB will bring it into read-only and mount mode depending on the Data Guard type (Active Data Guard / Regular Data Guard).
Considerations
- Enhanced PDB automation is supported on database releases 19c and later.
- PDB clone (remote, refreshable) and relocate are supported across the Compartment, VM Cluster, DB System (BaseDB), VCN, Network (ExaDB-C@C), and database version (same or higher). The same is not supported across the Availability Domain (AD) and Exadata Infrastructure.
- A Data Guard standby cannot be either a source or a destination for the PDB clone and PDB relocate operations.
- A refreshable clone PDB created on a Data Guard primary will not appear on standby - its existence will be deferred until converted to a regular PDB.
- Currently, PDB automation is supported for the databases using TDE wallet-based encryption (Oracle-managed keys).
Source: oracle.com










0 comments:
Post a Comment