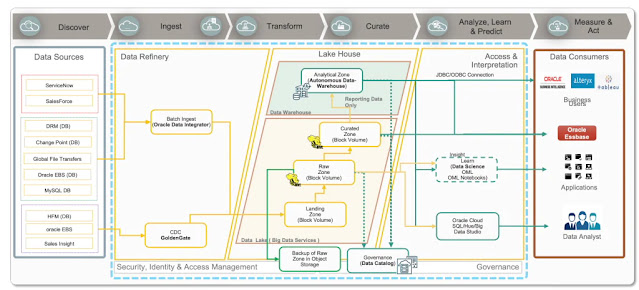
We are pleased to announce the
General Availability (GA) of support for Multiple VM Clusters and VM Cluster Node Subsetting capability on Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure (ExaDB-D). Previously, ExaDB-D customers could only create a single VM cluster on any given Exadata Infrastructure and the single cluster automatically spanned across all DB Servers in the infrastructure. With Multiple VM Clusters (Multi-VM) support and VM Cluster Node Subsetting capability, you can now create multiple VM Clusters on a single Exadata Infrastructure in ExaDB-D and have the flexibility to choose specific DB Servers within the infrastructure to host VMs from the cluster.
Key Customer Benefits
With the Multi-VM and VM Cluster Node Subsetting capability, you can now
◉ Provision a new VM cluster with any number of VMs rather than hosting a VM on each DB server in the Exadata Infrastructure.
◉ Start with a smaller VM cluster size at provisioning time, thereby enabling cost savings on resources allocated per VM.
◉ Expand the VM clusters to add VMs on-demand providing flexibility to scale resources without disrupting current running workloads.
◉ Shrink the VM clusters to remove VMs as needed to ensure efficient allocation of DB server resources.
◉ Isolate VM clusters to run on specific DB Servers giving complete control over the isolation strategy for mission-critical workloads.
◉ Co-locate VM clusters on specific DB Servers to implement efficient consolidation and streamline maintenance across various workloads.
◉ Allocate resources from the new generation of DB servers to provision new VM clusters or extend the existing VM clusters to ensure optimal utilization of available resources.
OCI Console Experience
Let's go over the following core user journey highlights related to Multi-VM and VM Cluster Node Subsetting using the OCI console.
◉ Provision VM cluster on a subset of DB Servers
◉ Add or remove VM(s) to scale VM Cluster
◉ Scale VM resources allocated to a provisioned VM cluster
◉ Scale Infrastructure with multiple VM Clusters
1. Provision VM Cluster on a subset of DB Servers
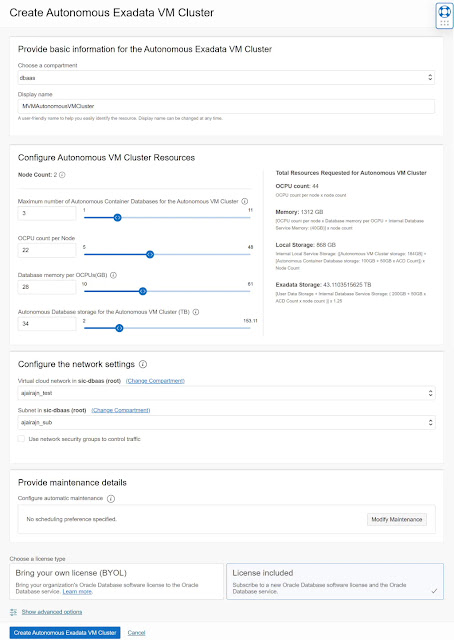
On the Exadata Infrastructure details page, you can navigate to the VM Cluster section and initiate the create VM Cluster workflow to provision a new cluster on this infrastructure.
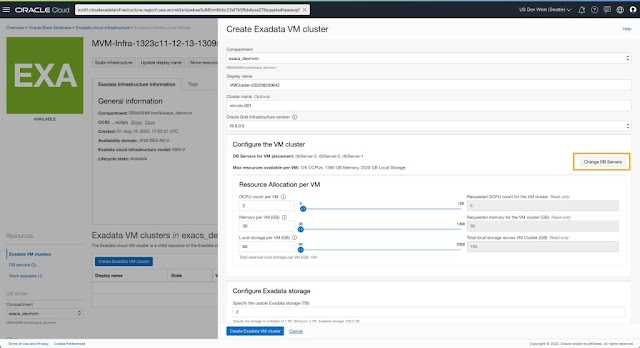
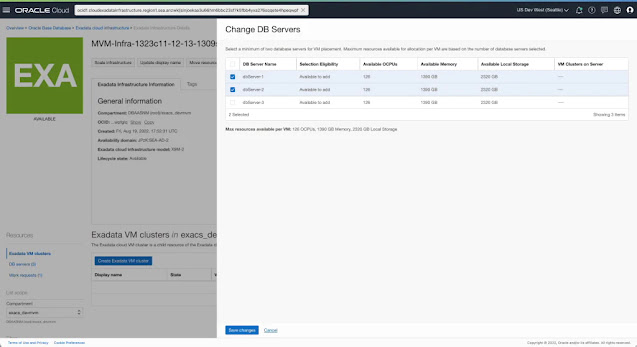
The create VM Cluster workflow now includes selecting the DB servers on which you want to host the VMs for the new cluster. By default, the create VM Cluster flow selects all the DB Servers in the infrastructure. You can change this selection to pick a subset of DB Servers to host VMs for the cluster.
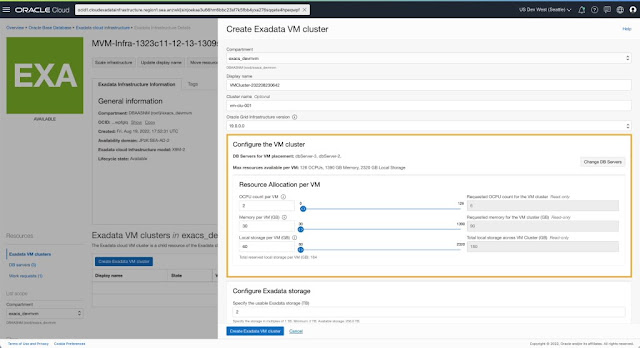
You can specify the placement of each VM in the cluster by selecting the DB server to host the VM for this cluster. All DB Servers part of the Exadata Infrastructure are listed and available for selection to place a VM. You can see the available OCPU, memory, and local storage resources for each DB server, along with the list of existing VM clusters already hosting VMs on the respective DB Servers. Based on the isolation and co-location preferences and planned resource allocation limits, you can choose the DB servers best suited for their specific use case to be part of this VM cluster.
Once the DB servers to host VMs for the cluster are selected, you can specify the allocation for OCPU, memory, and local file system storage resources per VM using the presented controls. The maximum resources available for assignment per VM depend on the selected DB servers that will host these VMs for the cluster. The DB server with the least resources will determine the maximum limit available for allocation per VM, given the symmetric resource allocation across all VMs in the cluster.
You can now specify the Exadata Storage allocation as part of the create VM Cluster flow.
The VM cluster details page shows the total number of VMs and the total resources allocated across all VMs after the provisioning completes successfully. You can also view the list of VMs in the cluster and their respective resource allocation, IP addresses, and a hyperlink to view the DB Server hosting the VM. The DB server details page will list all the VMs from various clusters hosted on that DB Server.
2. Add or remove VM(s) to scale VM Cluster
2.1 Expand a provisioned VM Cluster by adding VM(s)
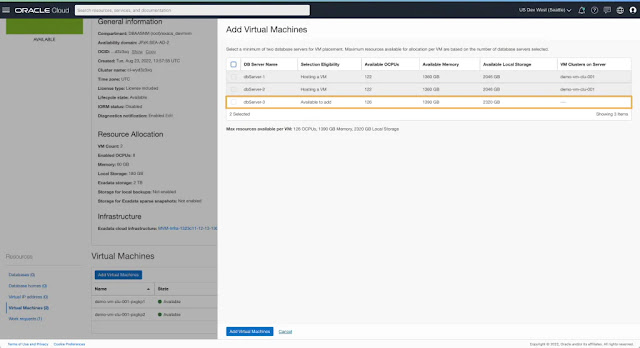
You can expand a provisioned cluster on-demand by adding VMs from the cluster details page.
While adding new VMs to a provisioned cluster, you can choose the specific DB servers on which you want to add new VMs and extend the VM Cluster. DB servers already hosting a VM from a particular cluster are not available to host another VM from the same cluster. For every DB Server, you can see the available OCPU, memory, and local storage along with the list of VM clusters hosting VMs on that DB server. Based on the information presented, you can choose the DB server(s) best suited to host the newly added VM(s).
Note: Newly added VMs will have the same resource allocation for OCPU, memory, and local storage as existing VMs part of the cluster.
Total resources allocated across the cluster are updated to reflect the newly added VM resources. Each new VM added to the cluster is listed along with existing VMs and displays the allocated resources, IP addresses, and the DB server hosting the VM.
2.2. Shrink a provisioned VM Cluster by removing VM
Additionally, you can navigate to a specific VM listed as part of the cluster and use the action menu dropdown for the list row to terminate the VM.
Terminating a virtual machine will terminate any database instances running on the VM and requires additional confirmation to proceed.
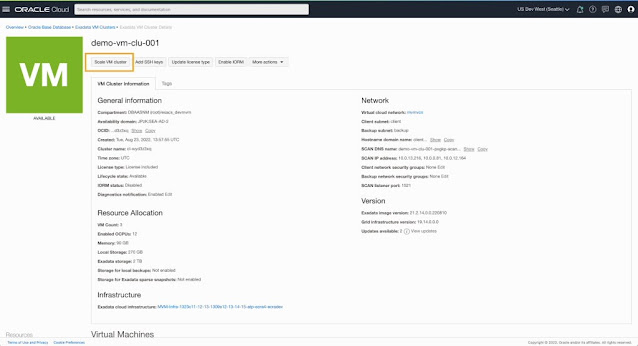
3. Scale VM resources allocated to a provisioned VM Cluster
For a provisioned VM cluster, you can always navigate to the cluster details page and initiate a scale action to change the resource allocation for the VMs in the cluster.
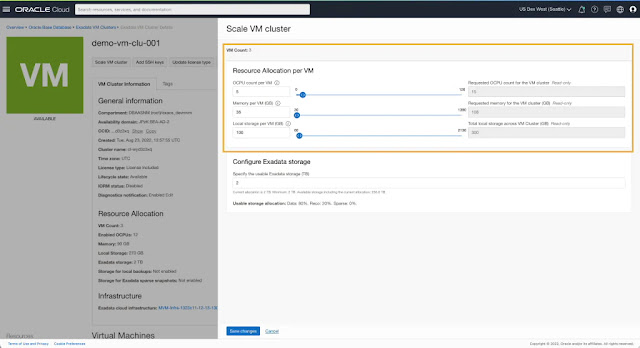
The scale VM cluster resources workflow shows the number of VMs that are part of the cluster and presents controls to change the allocation for OCPU, memory, and local file system storage resources per VM. You can view the total resources allocated across all VMs in the cluster as a read-only summary similar to the view shown during cluster creation.
4. Scale Infrastructure with multiple VM Clusters
4.1. Scale Infrastructure with Database Server
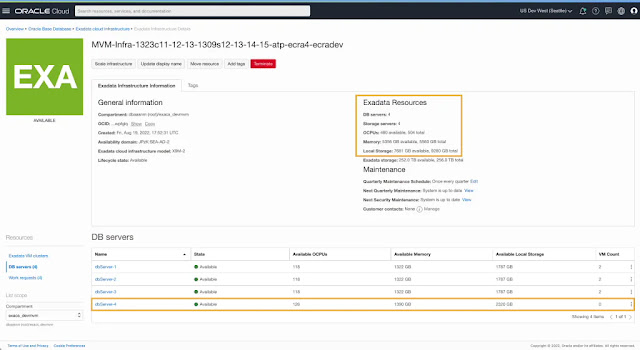
With Exadata Infrastructures now supporting multiple VM Clusters, adding a database server to the infrastructure makes the additional resources from the newly added DB server available to all VM Clusters. You can initiate a scale infrastructure operation from the infrastructure details page.
You can specify one or more DB servers to add as part of the scale infrastructure flow.
Once the DB Server is added to the infrastructure, all resources (OCPU, Memory & Local Storage) from the newly added DB Server are available and updated on the infrastructure details page. The newly added DB Server is listed alongside existing DB Servers already part of the infrastructure and is not assigned to any VM cluster.
The newly added DB Server is available to host a VM as part of the Create VM Cluster and Add Virtual Machine flows.
4.2. Scale Infrastructure with Storage Server
Adding a storage server to the infrastructure makes the additional storage capacity from the newly added server available to all VM Clusters. You can specify one or more storage servers to add as part of the scale infrastructure flow.
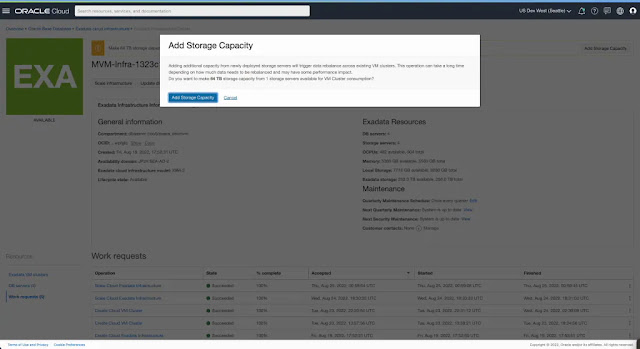
You can add the storage capacity from the newly added servers to the total usable Shared Exadata Storage capacity and make it available for VM Clusters to allocate and consume.
Adding storage capacity to the infrastructure's shared Exadata Storage capacity free pool triggers an ASM rebalance of existing disk groups (used by the provisioned VM Clusters) to all storage servers visible to the infrastructure, including the newly added ones.
Note: While rebalance is in progress, you may see some performance impact depending on how much capacity is already in use by the existing disk groups.
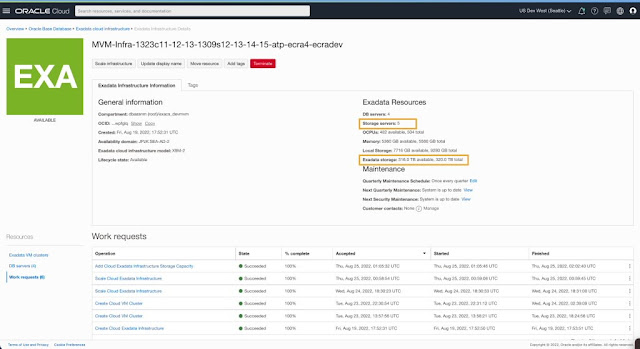
After completing all these steps for elastic storage expansion, you can view the total number of storage servers and the total Exadata Shared Storage capacity on the infrastructure details page.
As part of the VM Cluster scale workflow, you can allocate and use the additional storage capacity from the newly added storage server(s). The new maximum limit for shared storage capacity is reflected and used for validation.
Note: The additional storage capacity from the newly added storage server(s) is also presented and available as part of the workflow to create new VM Clusters.