We are excited to announce that customers can now take advantage of Kubernetes and Docker based deployment for sharded databases starting with Oracle Database 21c (21.3).
Oracle Sharding distributes segments of a data set across many databases (shards) on independent compute resources, on-premises, or in the cloud. It enables globally distributed, linearly scalable, multi-model databases. It requires no specialized hardware or software. Oracle Sharding does all of this while providing strong consistency, the full power of SQL, support for structured and unstructured data, and the Oracle Database ecosystem (SQL Developer, Enterprise Manager Cloud Control, RMAN, and Data Pump). Oracle Sharding meets data sovereignty requirements and supports applications that require low latency and high availability.
Oracle Sharding on Kubernetes
With many Oracle customers already using Kubernetes to deploy applications and databases, there is an increase in demand to manage large datasets with high-throughputs, and this is where Oracle Sharding can be very useful because it brings extreme scalability, fault isolation, and geographical distribution of data by distributing the data set across different shards.
Oracle Sharding on Kubernetes uses StatefulSet to provide stable, unique network identifiers and stable, persistent storage so you can create and manage your Oracle Sharding replica set natively in Kubernetes with Oracle supported helm and chart templates. Data is stored on a persistent volume so when a pod is recreated, all the data is still there. Some of the other benefits of running Oracle Sharding on Kubernetes are as follows:
◉ Quick deployments using pre-built configurations
◉ Rapid provisioning and de-provisioning of Oracle Sharding makes CI/CD integration easier
◉ Self-monitoring for pod-failures
◉ Elasticity (scale-in and scale out) without losing data
◉ Seamless lifecycle management including patching
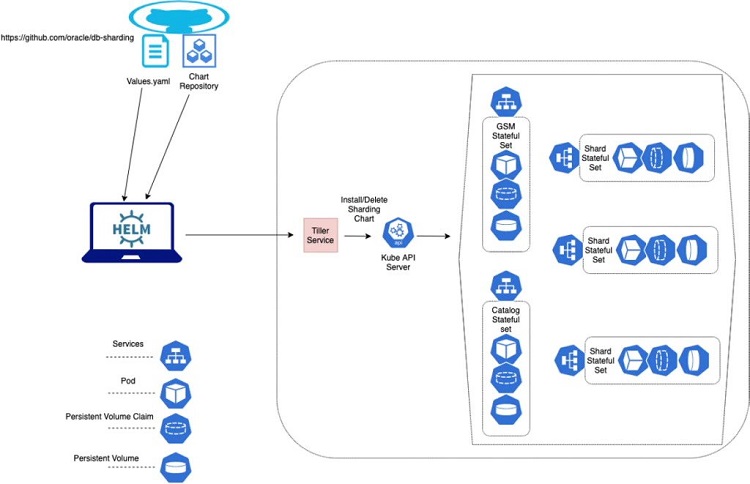
The architecture diagram below provides an overview of Oracle Sharding deployment on Kubernetes for both on-premise and cloud. To get started with Oracle Sharding on Kubernetes, follow the instructions on GitHub.



0 comments:
Post a Comment