Simpler database development experience
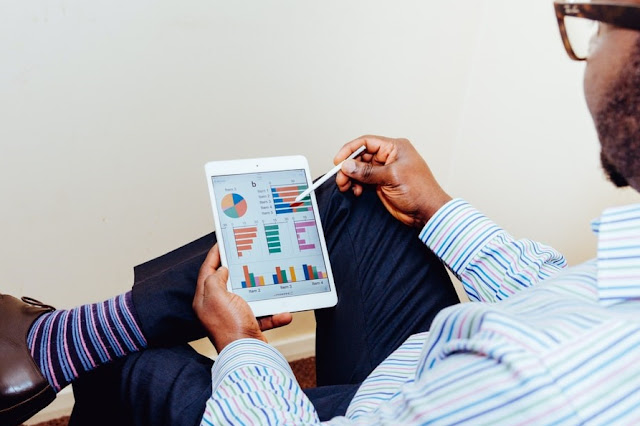
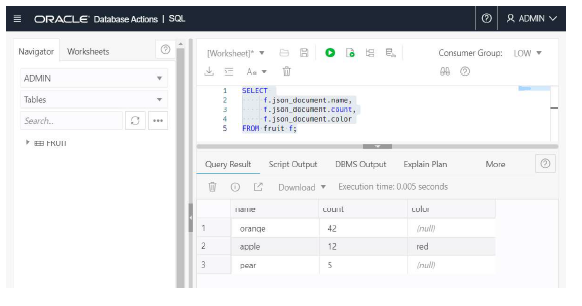
Developers like simplicity in building applications using choice of programming languages, frameworks, tools and databases. Document databases have become a popular choice for storing and processing application data in a language independent Java Script Object Notation (JSON) documents as a collection.
Document databases offer simple APIs for CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete) and frameworks that make it easy to persist application objects. This allows developers to focus on the application logic in microservices / API driven architecture without having to learn SQL (Structured Query Language).
Easily adapt to application changes
Unlike relational database models where application objects are mapped to database tables with predefined set of columns a.k.a schema, JSON documents are schema-flexible and allows values in each document to vary throughout a collection, making them ideal for Agile development methodology.
Further, JSON supports nested structures that can be used to selectively add redundant data, so it can be read and written as a single unit to avoid joins and multiple DML (Data Manipulative Language) statements when reading or writing an application object.
Finally, document database architecture provides internet scale applications required performance and scalability with scale-out storage and compute capacity with minimum response time from database. Document databases typically provide single-digit millisecond latencies for small reads and writes, while serving 1000s of concurrent users.
Document Databases are great, but...
MongoDB has popularized document databases for developers with their free to use community edition. MongoDB offers simple document database APIs; however, it has limitations supporting multi-document ACID transactions critical to enterprise applications. For developers, implementing basic SQL engine functionality requires writing, testing and maintaining hundreds of lines of application code, resulting in security vulnerabilities, increased development time and maintenance.
As the use cases for the applications change, supporting additional data types, workload types require external integration with other single-purpose databases such as Graph, Spatial etc, potentially using different APIs and need to move the data to those databases, resulting in data fragmentation, data inconsistency and security risks.
Keeping it together with converged database
Oracle's converged database has built-in support for all modern data types and the latest development paradigms. Converged databases support spatial data for location awareness, JSON for document stores, IoT for device integration, in-memory technologies for real-time analytics, and of course, traditional relational data. By providing support for various data types, a converged database can run all sorts of workloads from IoT to Blockchain to Analytics and Machine Learning. It can also handle various development paradigms, including Microservices, Events, REST, SaaS, and CI/CD eliminating data replication or duplication, reducing the cost and increasing developer productivity.