To maintain the information in up-to-date state we might need the following commands
To register manual backups
Suppose we have taken a backup of a particular datafile outside of RMAN through O/s commands. Whatever backup you take outside of RMAN, RMAN will not know about it and it will not consider this backup exist until we register the backup in RMAN catalog.
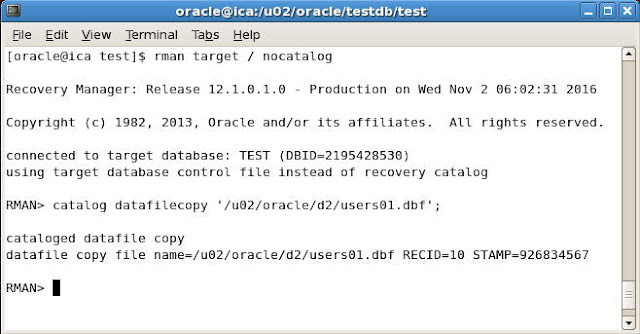
For example suppose we have taken a backup of users01.dbf datafile on /u02/oracle/d2/users01.dbf' directory and now we want to register this backup in RMAN repository
To register give the following command
RMAN> catalog datafilecopy '/u02/oracle/d2/users01.dbf';
Once you issue the above command then RMAN will enter the information about this backup in the catalog and will recover from it in future recovery operation if needed.
Crosscheck Command in RMAN
Crosscheck is a very useful command in RMAN which automatically checks all the backups whose information is store in the RMAN repository and whether they are available on the disk or not.
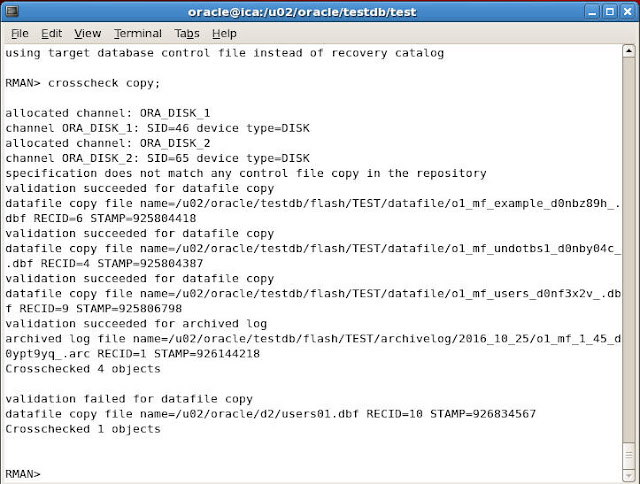
If a corresponding backup is not available on the disk then Crosscheck command marks the backup as Expired otherwise it marks it as Available
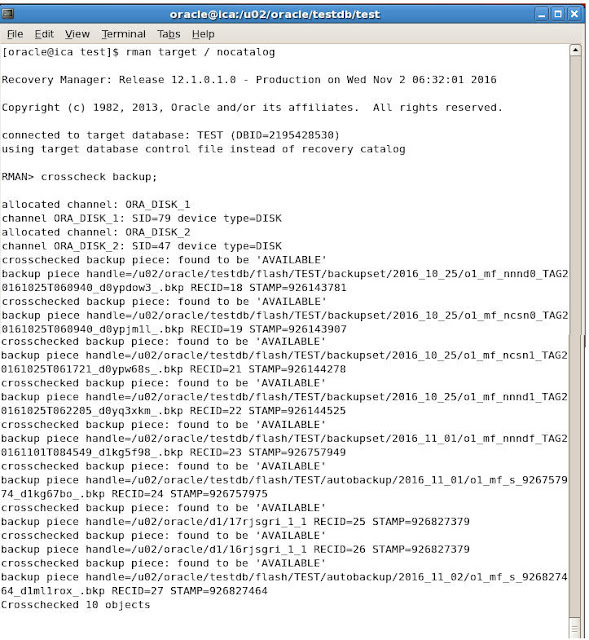
To check status of all backupsets we can give the following command
RMAN> crosscheck backup;
To check status of all image copies we can give the following command
RMAN> crosscheck copy;
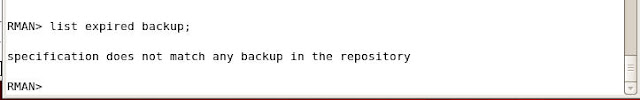
To know the status of Expired and Available backupsets give the following command
RMAN> list expired backup;
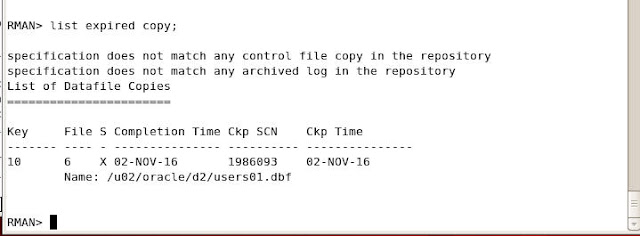
To know the status unavailable image copy copy give the following command
RMAN> list expired copy;
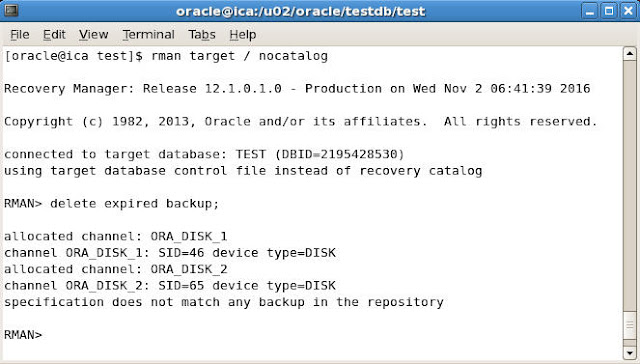
To delete the expired backup sets we can give the following command
RMAN> delete expired backup
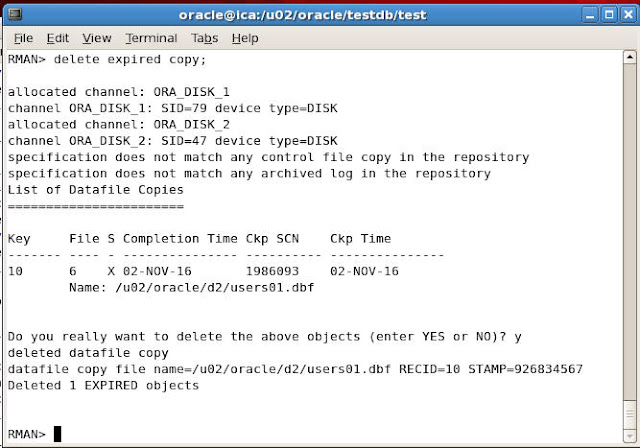
To delete the expired image copies we can give the following command
RMAN> delete expired copy;



0 comments:
Post a Comment